- Joined
- Nov 9, 2025
- Posts
- 555
- Reputation
- 807
THIS IS A REPOST AS OTHER ONE HAD MISTAKES
Some music you can listen to whilst reading -
The human skull is made up of 22 bones, 14 of them make up the face. These bones give shape to the face, protect sensory organs, and anchor muscles that allow for chewing, speaking, and expression.
How Facial Bones Shape Appearance:
Overall facial shape
- Oval, round, heart-shaped, square
- Based mostly on mandible and zygomatic structure
Profile
- Maxilla and mandible projection
- Nasal bone height
- Forehead slope
Eye shape
- Orbit size and orientation
- Lacrimal bone and zygomatic position
Nose structure
- Nasal bones + cartilage shape
Cheek fullness and contour
- Zygomatic bones + soft tissue
Below is a breakdown of each major facial bone.
Some music you can listen to whilst reading -
The human skull is made up of 22 bones, 14 of them make up the face. These bones give shape to the face, protect sensory organs, and anchor muscles that allow for chewing, speaking, and expression.
How Facial Bones Shape Appearance:
Overall facial shape
- Oval, round, heart-shaped, square
- Based mostly on mandible and zygomatic structure
Profile
- Maxilla and mandible projection
- Nasal bone height
- Forehead slope
Eye shape
- Orbit size and orientation
- Lacrimal bone and zygomatic position
Nose structure
- Nasal bones + cartilage shape
Cheek fullness and contour
- Zygomatic bones + soft tissue
Below is a breakdown of each major facial bone.
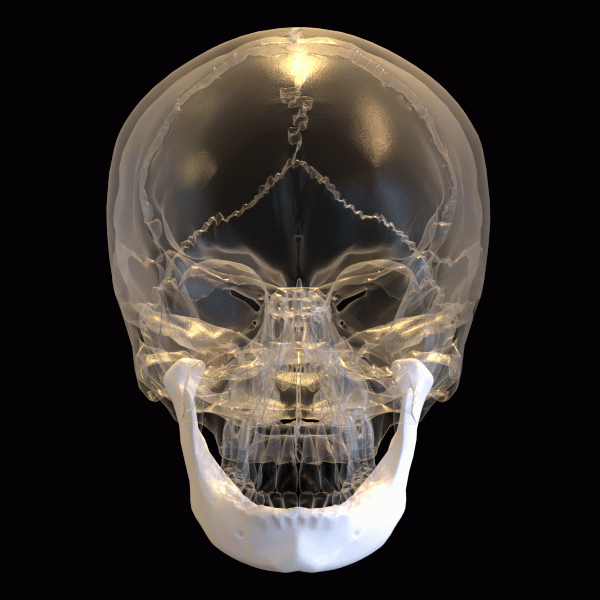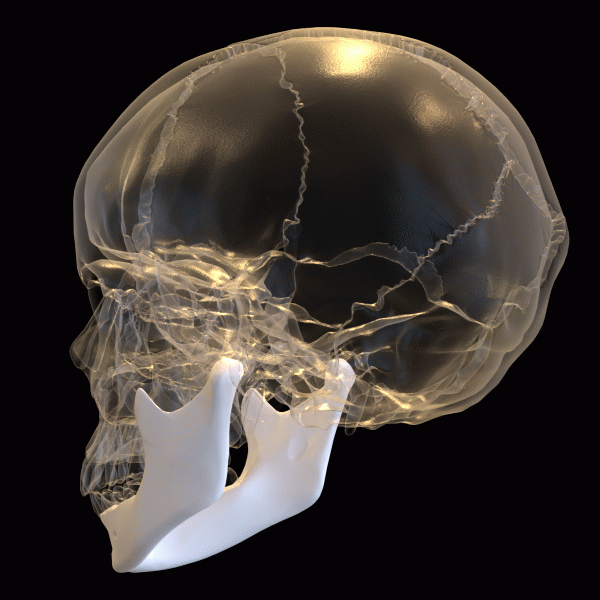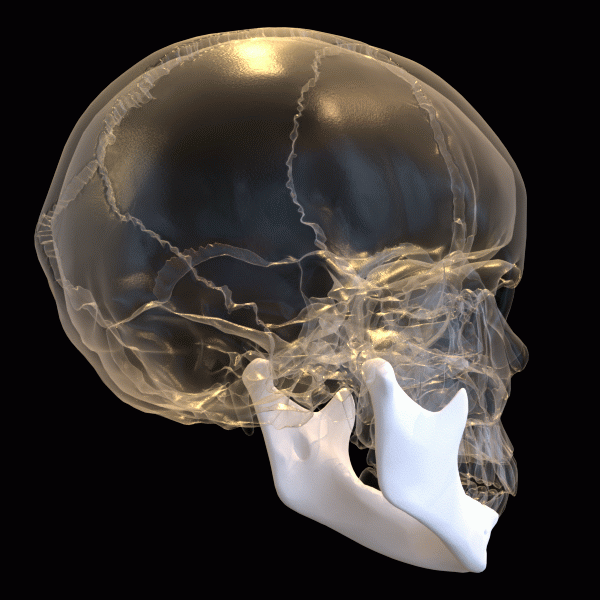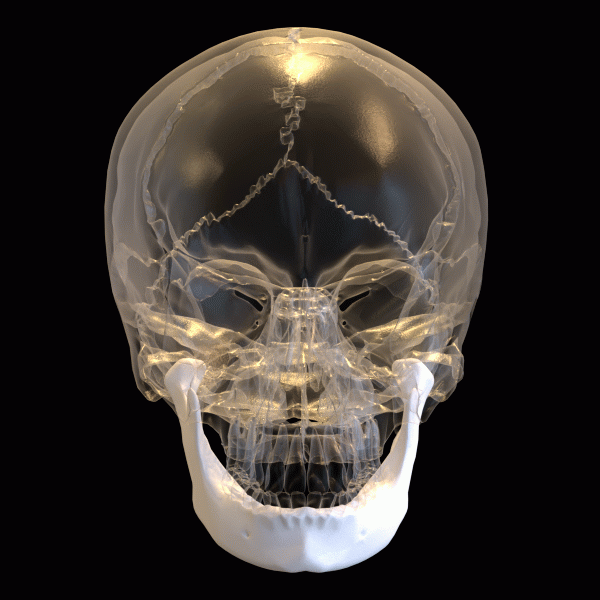
Mandible (Lower Jaw)
Where it is: The lower jaw bone; the only movable bone in the skull.

What it determines:
- Jawline Shape
- Chin projection
- Lower facial height
- Bite/occlusion (how teeth meet)
Where it is: The lower jaw bone; the only movable bone in the skull.


What it determines:
- Jawline Shape
- Chin projection
- Lower facial height
- Bite/occlusion (how teeth meet)
Maxilla (Upper Jaw)
Where it is: Forms the upper jaw, part of the cheeks, nasal cavity, and hard palate.


What it determines:
- Midface projection
- Cheek contour
- Upper lip support
- Nasal base shape
- Tooth alignment and smile aesthetics
Where it is: Forms the upper jaw, part of the cheeks, nasal cavity, and hard palate.


What it determines:
- Midface projection
- Cheek contour
- Upper lip support
- Nasal base shape
- Tooth alignment and smile aesthetics
Zygomatic Bones (Cheekbones)
Where they are: Lateral upper cheeks, connecting to maxilla, temporal bone, and frontal bone.


What they determine:
- Cheekbone prominence
- Facial width
- High/low cheekbone appearance
- "Model-esque" angular contour
Where they are: Lateral upper cheeks, connecting to maxilla, temporal bone, and frontal bone.


What they determine:
- Cheekbone prominence
- Facial width
- High/low cheekbone appearance
- "Model-esque" angular contour
Nasal Bones
Where they are: Two small bones forming the bridge of the nose.


What they determine:
- Height and shape of the nasal bridge
- Nose profile (flat, high, straight)
- Structural support for the upper nose
Where they are: Two small bones forming the bridge of the nose.


What they determine:
- Height and shape of the nasal bridge
- Nose profile (flat, high, straight)
- Structural support for the upper nose
Lacrimal Bones
Where they are: Tiny bones forming part of the inner eye socket near the tear ducts.


What they determine:
- Tear duct location
- Depth of the inner eye corner
- Affects eye shape subtly
Where they are: Tiny bones forming part of the inner eye socket near the tear ducts.


What they determine:
- Tear duct location
- Depth of the inner eye corner
- Affects eye shape subtly
Palatine Bones
Where they are: Behind the maxilla, forming part of the hard palate and nasal cavity.


What they determine:
- Palate shape
- Nasal cavity width
- Speech resonance and airway structure
Where they are: Behind the maxilla, forming part of the hard palate and nasal cavity.


What they determine:
- Palate shape
- Nasal cavity width
- Speech resonance and airway structure
Inferior Nasal Conchae
Where they are: Curved bones inside the nasal cavity on each side.

What they determine:
- Airflow efficiency
- Humidification of inhaled air
- Minimal influence on external appearance
Where they are: Curved bones inside the nasal cavity on each side.

What they determine:
- Airflow efficiency
- Humidification of inhaled air
- Minimal influence on external appearance
Vomer
Where it is: Thin bone forming the lower part of the nasal septum.

What it determines:
- Nasal septal alignment
- Whether the nose deviates to one side
- Nasal airflow
Where it is: Thin bone forming the lower part of the nasal septum.

What it determines:
- Nasal septal alignment
- Whether the nose deviates to one side
- Nasal airflow
Frontal Bone
Where it is: Technically part of the cranial vault, but visibly facial.


What it determines:
- Forehead slope and height
- Brow ridge prominence
- Upper facial contour
Where it is: Technically part of the cranial vault, but visibly facial.


What it determines:
- Forehead slope and height
- Brow ridge prominence
- Upper facial contour
Temporal Bones
Where they are: Forms the temple areas.


What they determine:
- Side-of-head contour
- Cheekbone extensions
Where they are: Forms the temple areas.


What they determine:
- Side-of-head contour
- Cheekbone extensions
| Bone | Location | Main Appearance Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Mandible | Lower jaw | Jawline, chin shape |
| Maxilla | Upper jaw | Midface projection, smile, nasal base |
| Zygomatic | Cheekbones | Facial width, cheek contour |
| Nasal bones | Nose bridge | Shape/profile of nose |
| Lacrimal | Inner eye socket | Subtle influence on eye shape |
| Palatine | Hard palate | Effects speech, airway |
| Inferior nasal conchae | Inside nose | Airflow |
| Vomer | Nasal septum | Nose deviation, airflow |
| Frontal | Forehead | Brow slope, upper face shape |
| Temporal | Temples | Side contour of skull |
Thank you for reading! If you found this helpful, rep this post.


 bump
bump